Growth Factor-free Proliferation & Differentiation of Stem Cell
KEY INFORMATION
Healthcare - Pharmaceuticals & Therapeutics
TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW
Stem cell therapy is one of the most promising potential treatments for neurodegenerative diseases. It involves cultivating stem cells for differentiation into new and healthy cells, which can then be transplanted to the human body to replace damaged or dead cells.
The conventional methods for cultivating stem cells typically require the use of animals and biochemical growth factors that may also encourage the growth of cancer cells. These methods are costly and the cells produced are often cancerous.
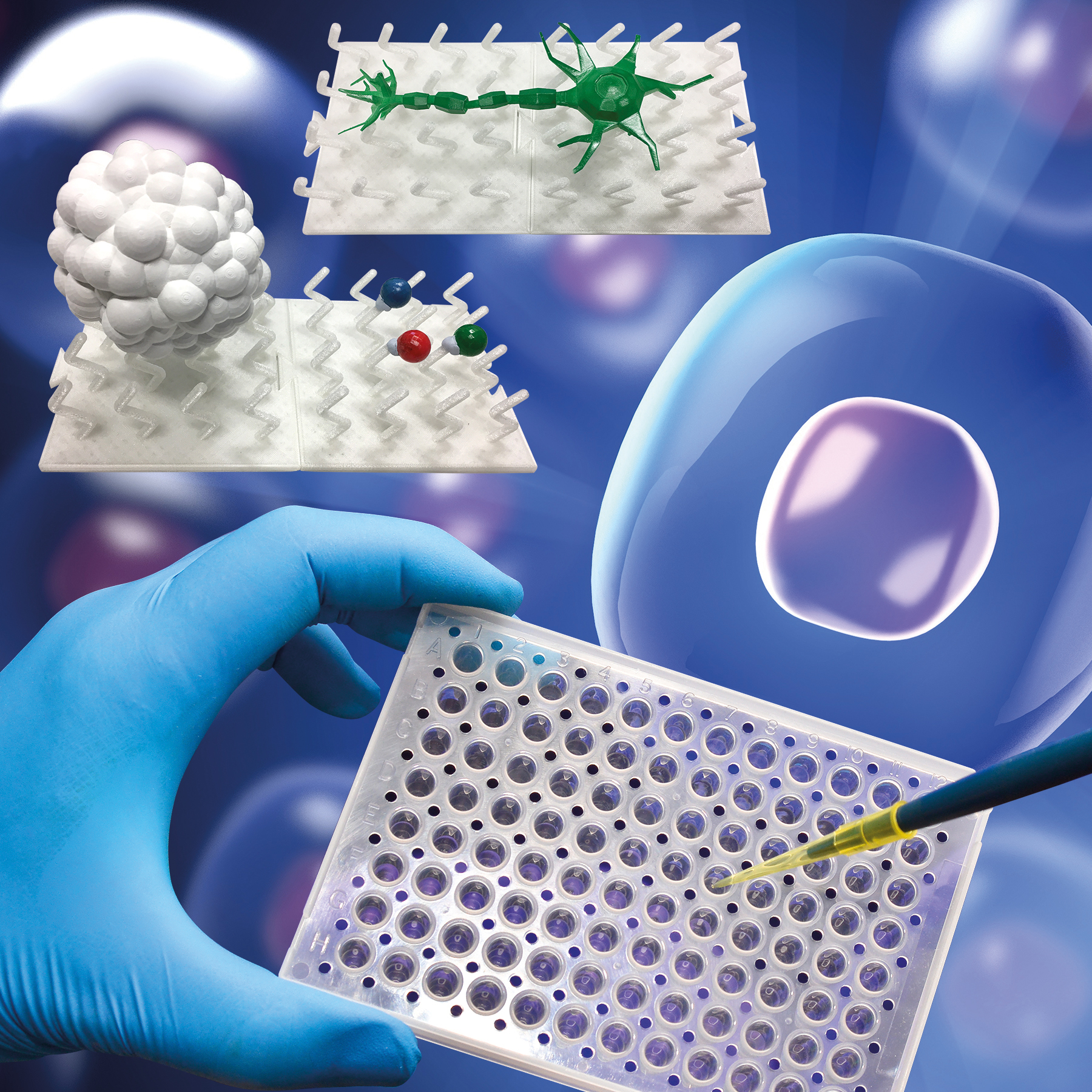
The technology is a method for growing stem cells without the need for animals or biochemical factors. The device, called inorganic sculptured extracellular nanomatrices (iSECnMs), uses nanoscopic structures on its surfaces to stimulate growth and differentiation of stem cells by physical stimulation as well as inhibit other directors of differentiation. Thus, it substantially reduces the risk of inflammation or cancer cell formation. The material is biocompatible and low-cost, so the device is well-suited for mass production. The technology could generate healthy and functional cells for use in regenerative therapy, as well as treatment for neurodegenerative, chronic and joint diseases.
TECHNOLOGY FEATURES & SPECIFICATIONS
Technology features include:
- High biosafety level
- Controllable stem cell differentiation
- Suitable for mass production
- Stronger functions of cultured neurons
- The cell growth rate of using this technology is more or less than the same as the current methods with growth factors
By varying the stiffness, density and arrangement of the nanostructures, or the shape of the matrix layer, the stem cells can be differentiated into different desirable functional cells.
This technology is feasible to be applied to human because:
1. The materials which the iSECnMs are composed of have been well demonstrated to be biocompatible with no toxicity;
2. The neural stem cell differentiation on the iSECnMs will be operated outside the human body.
POTENTIAL APPLICATIONS
Areas where the technology can be applied include the following:
- Research institutions and laboratories to develop stem cell therapy,
- Clinics and hospitals, and
- Therapeutic agents to cure some diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.
The team has plans to extract the patient’s neural stem cells and develop them into a therapeutic agent for incurable diseases for clinical tests.
Unique Value Proposition
New opportunities for incurable diseases:
- This invention has shown great potential for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease and other incurable diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease and certain types of cancer.
- It could provide a safe platform for research into stem cell therapies using the latest, novel nanotechnology, and also help boost the development of regenerative medicine.
